Unlocking the Best of Both Worlds: Can Fiber Internet Go Wireless?
In the age of lightning-fast internet connections, the term “fiber-optic” is often hailed as the pinnacle of broadband technology, promising unparalleled speeds and reliability. But as our world continues to untether itself from cumbersome cables and embrace the convenience of wireless technologies, many wonder: Can fiber internet be wireless? It’s a question that beckons us to explore the intersection of two revolutionary technologies—fiber-optic and wireless internet. In this blog post, we will delve into the possibilities and limitations of marrying these two technologies, helping you understand how and when fiber internet can indeed go wireless. Stay tuned as we unravel the complexities and offer insights into this fascinating topic.

Can Fiber Internet Be Wireless?: Unraveling the Possibilities
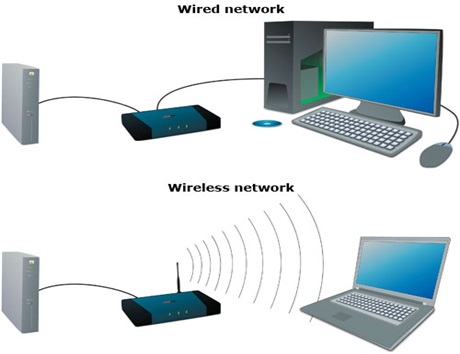
The question “Can fiber internet be wireless?” seems almost paradoxical at first. Fiber-optic internet is known for its high-speed data transfer over glass or plastic fibers, whereas wireless internet relies on radio waves to transmit data. At their core, these two technologies operate on entirely different mediums—one physical and the other intangible. However, when you start to delve into the realm of networking and data transfer, you’ll find that these technologies can indeed coexist, creating a synergy that leverages the strengths of both.
Fiber-optic internet is prized for its ability to transmit data at incredibly high speeds, often exceeding 1 Gbps, with some services even offering speeds up to 5 Gbps or more. This makes it an excellent backbone for any internet service, providing the high-speed and low-latency connection that users increasingly demand for activities like streaming high-definition videos, online gaming, and heavy file downloads. The catch is that fiber-optic cables must be physically laid down to connect locations, which can be a costly and time-consuming process.
Wireless internet, on the other hand, offers the convenience of cable-free connections. While its speeds might not match those of a direct fiber-optic connection, advancements in wireless technology—such as Wi-Fi 6 and the forthcoming Wi-Fi 7—have significantly improved the potential speeds and reliability of wireless networks.
How do these technologies converge?
The answer lies in the setup of your home or office network. A fiber-optic cable could be run to your location to provide the high-speed internet connection that fiber is known for. This cable would typically connect to a fiber-optic modem, converting the optical signals into electrical ones. From there, you could connect a wireless router to the modem, effectively transforming your high-speed, fiber-optic connection into a wireless one. This setup allows you to enjoy the best of both worlds: the blazing speed and reliability of fiber-optic internet, along with the convenience and flexibility of a wireless network.
Moreover, Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are increasingly offering integrated modem-router devices capable of delivering fiber-optic speeds over a wireless network. These devices are optimized to ensure minimal loss of speed and latency, thus bringing you closer to experiencing the full potential of your fiber-optic connection, wirelessly.
It’s also worth noting that emerging technologies like 5G are set to further blur the lines between fiber and wireless internet. 5G technology promises fiber-like speeds and is expected to rely heavily on fiber-optic backbones for its infrastructure. As 5G networks become more widespread, we might find that the distinction between fiber and wireless internet becomes less significant, offering users a seamless, high-speed experience irrespective of the medium.
Understanding Fiber Internet: A Wired Connection Like No Other
Fiber-optic internet stands as a technological marvel in the world of digital communications, offering a wired connection that is fundamentally different from traditional broadband options like DSL or cable. Crafted from bundles of glass or plastic fibers, this type of internet uses light signals to transmit data, resulting in an ultra-fast and reliable connection that has redefined our expectations of what broadband can do.
The underlying science of fiber-optic internet is rooted in the principles of light transmission. Unlike copper cables, which use electrical signals, fiber-optic cables transmit data in the form of light pulses. This key difference has several major implications. First and foremost, light is less susceptible to interference and attenuation over long distances compared to electrical signals. This results in a connection that not only offers higher speeds but also maintains those speeds over much greater distances. That’s why you’ll often find fiber-optic cables laid out for transcontinental and even transoceanic data links.
Speed Capabilities
The speed capabilities of fiber are astounding, ranging from 250 Mbps to 5 Gbps or even more in some cases. This makes it incredibly useful for modern-day applications that require large bandwidth, such as streaming 4K videos, conducting high-definition video conferencing, and handling complex cloud-based applications. And it’s not just the download speeds that are impressive; fiber-optic internet typically offers symmetrical speeds, meaning that upload speeds match download speeds. This is particularly beneficial for activities like uploading large files or live streaming.
Benefits of Fiber optic
One of the inherent benefits of fiber-optic internet is its low latency. Latency refers to the delay in the time it takes for data to travel from its source to its destination. Lower latency is crucial for activities like online gaming and real-time communication, where even a millisecond delay can make a huge difference. Because fiber-optic technology can transmit data almost at the speed of light, it achieves very low latency levels that are hard to match by other types of connections.
However, the exceptional performance of fiber internet does come at a price, both literally and metaphorically. Installing fiber-optic cables can be an expensive and labour-intensive process, requiring careful handling to prevent any damage to the delicate fibers. This is why fiber-optic internet is not yet universally available and is often found in urban and suburban areas where the cost of laying the infrastructure can be justified by high demand. Furthermore, fiber-optic internet plans are generally more expensive than their DSL or cable counterparts, although many argue that the cost is justified by the unparalleled performance.
It’s also worth noting that while fiber-optic internet is extraordinarily reliable, it’s not entirely immune to issues. Physical damage to the cables can disrupt the service, and like any other technology, it’s subject to equipment failures and maintenance outages. However, these occurrences are relatively rare and are far outweighed by the numerous advantages that fiber offers.
The Difference Between Fiber Internet and Wireless Internet
Fiber internet and wireless internet represent two distinctly different approaches to providing high-speed internet access, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks. While both technologies aim to offer fast and reliable connectivity, the methods by which they deliver this service are fundamentally different, affecting everything from speed and reliability to infrastructure requirements and cost.
Fiber Internet
Fiber internet, this technology uses bundles of optical fibers to transmit data via light signals. The most distinctive feature of fiber-optic technology is its ability to deliver extremely high data speeds, often reaching up to 1 Gbps or more for residential services, and even higher for commercial or specialized use. Speed isn’t the only advantage; fiber also offers low latency, which means a shorter delay time in data being sent or received. This is particularly beneficial for real-time applications like online gaming or video conferencing. Fiber internet is also highly reliable, not being prone to electromagnetic interference, and offers symmetrical upload and download speeds. However, the downside is that it’s often more expensive to install and maintain. The service area can be limited, particularly in rural locations, due to the high cost of laying fiber-optic cables.
Wireless Internet
Wireless internet, on the other hand, eliminates the need for any physical connection between the service provider and the user. Data is transmitted over radio waves, which means that users only need a modem and a Wi-Fi router to access the internet. The most obvious advantage of wireless internet is its convenience; there’s no need to run cables throughout your home, and you can easily connect multiple devices, including mobile phones and smart home gadgets. The new wireless standards like Wi-Fi 6 and the upcoming Wi-Fi 7 promise significantly higher speeds and better performance, making wireless internet a viable option for many households and businesses. Wireless internet is also easier and often cheaper to set up, especially in areas where laying physical cables would be impractical.
However, wireless internet does have its own set of challenges. Speeds can be inconsistent and generally slower than fiber, especially during peak times when many users are connected to the same network. Latency is also generally higher, which can affect the quality of real-time applications. Wireless connections are also more susceptible to various forms of interference, such as from other electronic devices or physical obstructions like walls and buildings.
Can Fiber Internet Be Delivered Wirelessly?
The question of whether fiber internet can be delivered wirelessly touches on an intriguing overlap between two fundamentally different technologies: fiber-optic and wireless internet. The short answer is yes, fiber internet can be “extended” wirelessly within a localized network, but the two technologies serve different segments of an internet connection pathway.
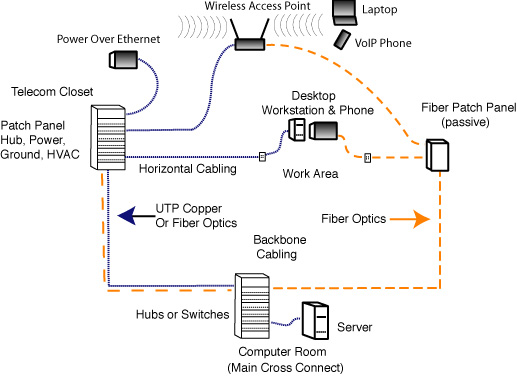
Here’s how it works: A fiber-optic line provides high-speed internet access to a specific endpoint—usually a home or business—by transmitting data as light pulses through a fiber-optic cable. Once the fiber-optic line reaches this endpoint, a fiber-optic modem converts these light signals into electrical signals that can be read by digital devices. At this stage, you can introduce wireless technology into the equation by connecting a Wi-Fi router to the modem. The router then takes the high-speed internet connection provided by the fiber-optic line and makes it accessible wirelessly to devices within its range. In this way, you’re essentially delivering fiber-speed internet wirelessly over a localized area.
Configuration
This configuration allows users to benefit from the high speeds and low latency of a fiber-optic connection while also enjoying the mobility and convenience of wireless internet. However, it’s crucial to note that this is a localized solution. The wireless extension of a fiber-optic connection is confined to the range of the Wi-Fi router, which is typically adequate for in-home or in-office use but not suitable for broader distribution.
Moreover, even the best Wi-Fi technologies will introduce some level of latency and potential speed reduction compared to a direct, wired fiber-optic connection. While advancements like Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E are narrowing this performance gap, the wireless segment is usually not quite as fast or as low-latency as the wired fiber-optic segment. Nevertheless, for most everyday applications like web browsing, streaming video, or video conferencing, this difference may be negligible to the average user.
To sum it up, while fiber-optic and wireless technologies serve different parts of the internet connection pathway, they can be combined to deliver a high-speed, fiber-based internet connection over a wireless network within a localized area. The union of these technologies offers users the speed and reliability of fiber with the convenience and mobility of wireless internet.
Can Fiber Internet Be Wireless?
Here are the key takeaways from the topic “Can Fiber Internet Be Wireless?” in a conversational tone, suitable for a 13-year-old:
- Fiber internet usually requires a physical connection through cables for optimal speed and reliability.
- However, some wireless technologies, like Wi-Fi, can be used to distribute fiber internet within a home or office.
- This allows devices to connect to the internet wirelessly without the need for individual wired connections.
- Wireless fiber internet can be convenient for mobile devices and areas where running cables is not feasible.
- It’s important to note that the actual fiber optic connection still needs to be wired to a wireless router or access point.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about wireless fiber internet:
1. How does fiber internet work?
Fiber internet uses fiber-optic cables made of thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light. These cables are capable of carrying large amounts of data at high speeds, resulting in faster internet connections compared to other types of connections, such as copper cables.
While fiber optic cables are used for the actual transmission of data, the connection to your devices can be either wired or wireless. So, while the data travels over the fiber cables, you can still enjoy a wireless connection within your home or office thanks to a router or modem that connects wirelessly to your devices.
2. Can fiber internet be wireless?
Although the actual connection from the internet service provider to your home or office needs to be done using fiber optic cables, the connection within your premises can be wireless. This is achieved by connecting a wireless router to the fiber optic modem, which then allows you to connect your devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and smart TVs, using Wi-Fi.
So, yes, fiber internet can be wireless once it enters your premises, providing the convenience of connecting multiple devices without the need for physical cables running throughout your home or office.
3. Is wireless fiber internet as fast as wired connections?
The speed of your internet connection depends on several factors, including your internet service provider’s plan, the quality of your router, and the number of devices connected to the network. In general, a wired connection tends to provide faster speeds compared to wireless connections.
However, with advancements in wireless technology, wireless fiber internet can still offer impressive speeds, especially when using the latest Wi-Fi standards. While a wired connection might still provide slightly faster speeds, wireless fiber internet can provide sufficient speed for most online activities, including streaming, gaming, and file downloads.
4. Are there any drawbacks to wireless fiber internet?
While wireless fiber internet offers convenience and flexibility, there are a few potential drawbacks to consider. One is that the signal strength can be affected by physical barriers such as walls and distance from the router. The farther you are from the router or the more obstructions between you and the router, the weaker the signal may be, potentially affecting your internet speed.
Additionally, wireless connections are generally more prone to interference from other devices, such as microwaves or neighbouring Wi-Fi networks. This interference can impact your internet speed and stability. However, by strategically placing the router and using Wi-Fi extenders or mesh systems, you can mitigate these issues and enjoy a reliable wireless fiber internet connection.
5. Can I get wireless fiber internet in my area?
The availability of wireless fiber internet depends on your location and the infrastructure in place. While fiber optic cables run from the internet service provider’s point of presence to local nodes, the last-mile connection to individual homes or businesses may still rely on traditional copper cables in some areas.
If your area has been upgraded with fiber-optic infrastructure, there’s a high chance that you can get wireless fiber internet. It’s best to check with local internet service providers to inquire about the availability of fiber internet and their wireless options in your specific location.

Cable vs. Fiber Internet Showdown – Watch This Before You Make Your Choice!
Summary
Fiber internet is super fast and reliable, but it usually requires cables to connect to your home. However, there are some wireless solutions available that can bring fiber-like speeds to your devices. These wireless options use a different technology called fixed wireless, which sends signals through the air. Although it might not be as fast as true fiber internet, it is a great alternative if you can’t get a wired connection in your area.
While wireless fiber solutions are convenient, they do have some limitations. The signal can be affected by things like distance, obstacles, and interference from other devices. Additionally, wireless technology may not be available in all areas, so it’s important to check with internet service providers to see if they offer this option. Overall, if you’re looking for fast internet without the hassle of cables, wireless fiber can be a viable solution.